Tokenization of real-world assets
Boson Protocol was founded in 2019 by Justin Banon and Gregor Boroša. Boson’s goal is to develop a platform that will enable companies and individuals to trade their products and services in a decentralized way with the help of blockchain technology. The decentralized public infrastructure for commerce that anyone can use. The platform will utilize NFTs and Ocean Protocol technology on the Polygon network.

So far, they have collected more than 35 million dollars from VCs and through the ICO.
Their ultimate goal is to change the way commerce works in the world today – moving from a centralized to a decentralized system. Through smart contracts and redeemable NFTs, Boson will improve users’ experiences and bring safer, faster, and cheaper trading while eliminating the need for a third party.

All of the above will come to life with the launch of the new V2 version of Boson’s protocol. V2 will include a new user interface, marketplace, and SDK, allowing independent developers to create their applications and stores within the Boson platform.
According to Boson, V2 will be released by the end of the year, while rumors suggest it is a matter of weeks rather than months.
NFTs on the blockchain will replace trading records stored in the databases of large companies.
How it will work in practice
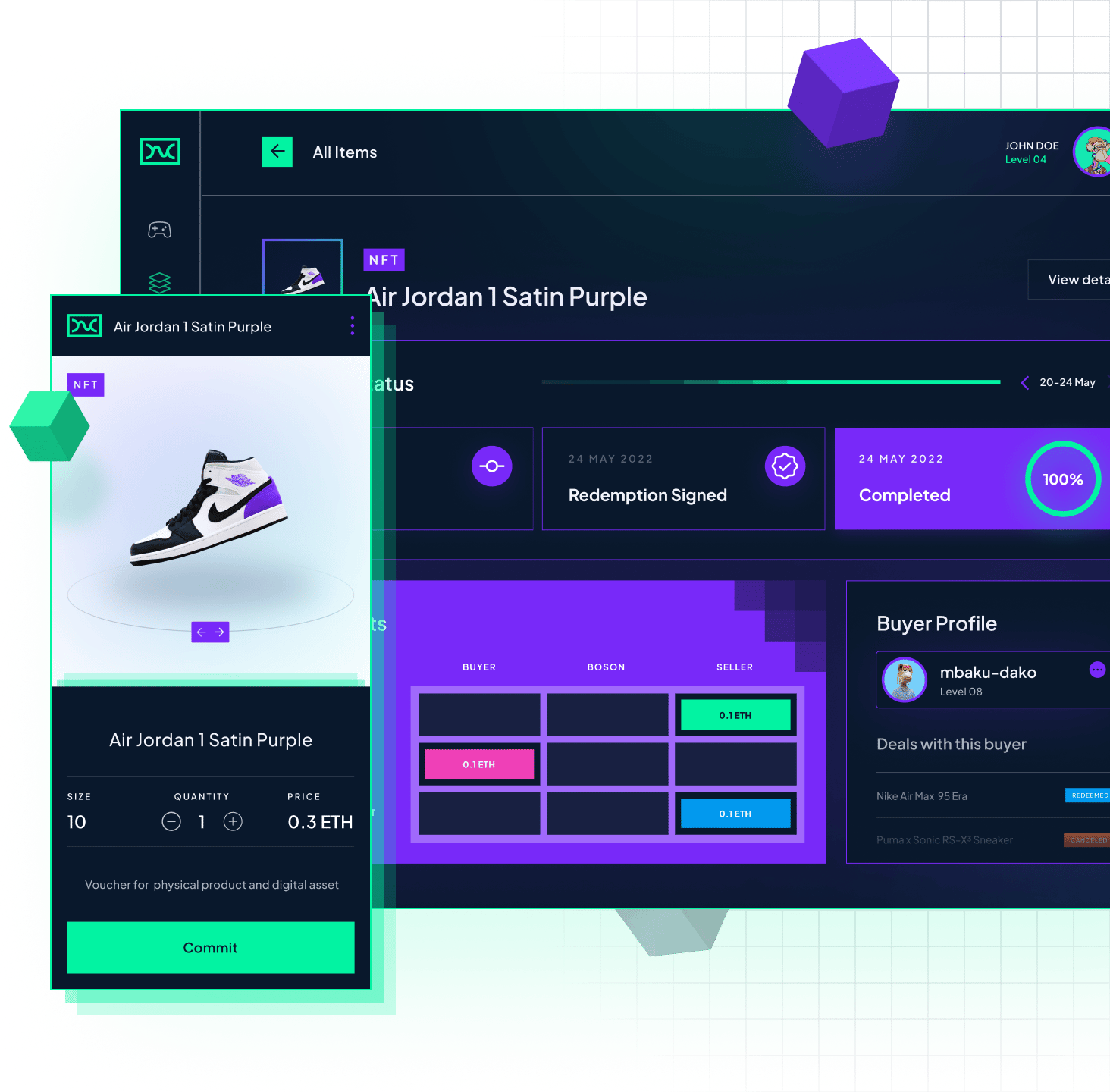
Let’s take a look at an actual example of the process. The seller wants to sell an item, for example, a guitar. The seller then creates an offer for the guitar. In addition to the price, he specifies other parameters, such as the necessary documents that will serve as proof of delivery. The seller also pays a deposit that serves as insurance if he does not deliver the item or abuses the system in another way. The amount of the deposit and other details are determined by the community through Boson DAO.
In the next step, the buyer sends money to the Boson smart contract and receives a redeemable NFT (a receipt for that item). NFT and Boson protocol guarantees the customer that he will get the guitar or his money back.
The buyer can sell this NFT on the open market (OpenSea) or on Boson’s marketplace, just like any other NFT token. He can use it as collateral, transfer it, keep it in his collection, or redeem it for the desired item/service (guitar).
When the buyer exchanges NFT for a guitar, the NFT is burned and the protocol releases the money to the seller.
Reselling items
If a buyer wants to resell the guitar, he will use the platform to create a new offer with an NFT. The newly created NFT will include a link to the previous NFT, which enables tracking the movement of that item through the platform.
Aside from individuals, Boson’s new platform allows companies/brands to create storefronts within the platform.
There are currently more than 40 brands interested.
Dispute resolution
If the customer has a complaint after receiving the service or product, he can file a dispute, which will be handled through a specially designed mechanism (Automated Mutual Resolution Process). It is expected that this mechanism will successfully resolve a majority of disputes. If the parties are still dissatisfied, they can escalate the dispute to a higher level. Here they will be able to use the services of a third party, such as Kleros (a decentralized arbitration service for resolving disputes in the Web3 economy) or some reputable eCommerce company. It is important to note that these companies’ roles are very limited, and their services will be used only for specific cases of dispute resolution – if the users choose to use them.

Fees, communication and user profiles
The Boson protocol will charge a 0,5% fee for its services. In comparison, OpenSea, the largest NFT marketplace, charges 2.5%. The Boson DAO community determines the fees through a voting mechanism. You can find the voting results here.
All fees are deposited into a DAO-managed treasury. Fees are designed to make the system self-sustaining.
Messages are exchanged between trading participants within the platform using the XMPT network for decentralized communication in the web3 space.
For user profiles, Boson uses Lens Protocol, the most advanced decentralized solution. Lens is an upgradeable web3 infrastructure for the next generation of social networks.

Royalties
The Boson platform is designed to ensure that sellers receive royalties from secondary sales. For example, if a seller sells a guitar to a buyer who resells it to another buyer, the seller will receive a percentage of the new sale as well.
This mechanism provides an additional incentive for sellers to use the Boson platform, while the platform incentivizes buyers through Boson’s safe delivery of purchased goods.
The Boson Protocol addresses one of Web3’s fundamental issues: how to mediate commerce transactions when selling real-world assets using smart contracts
$BOSON token
BOSON token is an integral part of the system. It has three basic functions:
- Governance
- Fee
- Incentivization
When managing the protocol, participants will decide on proposals by voting. Boson token gives its holders a right to give their vote. Voting is used to make decisions about how the Boson protocol should operate, including the distribution of assets owned by the DAO.
Fees (0.5%) for using the platform are charged exclusively in BOSON tokens.
The BOSON token is also used to incentivise actions in the system including stimulating supply and demand. Boson will distribute BOSON tokens to early adopters of the system.
On the Coingecko token page you can find the price, supply, markets, and other information about the token.
Smart contract audits
Because the V2 version of the Boson protocol differs significantly from the previous version, the smart contract was sent to Peckshield for revision. The report is available here.
In addition, the company Omniscia is undergoing an audit, which is still pending.
Conclusion
The new V2 version of the Boson protocol aims to change how commerce works today. They appear to have a good foundation for market success with a well-rounded approach that includes detailed mechanisms for executing sales processes, dispute resolution, and decentralized management. What I see as the most significant challenges will be effectively resolving fraud, a pain point of online sales, and establishing a good management model, which is not easy for any crypto project. It remains to be seen how everything will play out in practice.
More information about how the system works can be found in their whitepaper.
Vedran Mijatović

